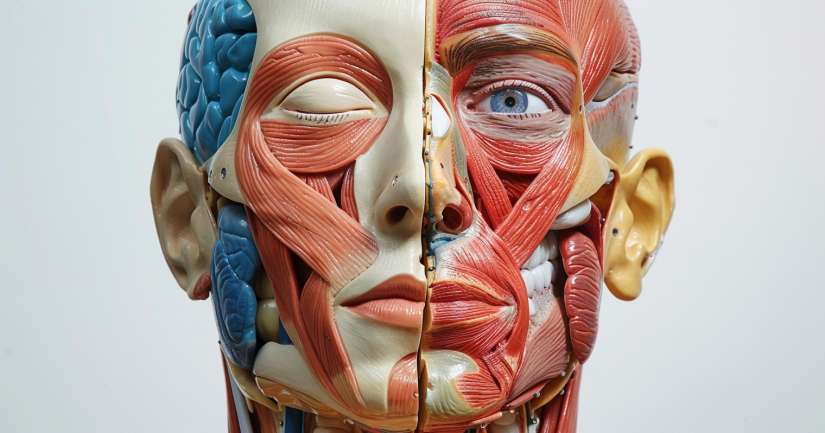
From the tip of the nose to the soles of your feet, the Body Parts Anatomy Quiz brings together the key external and internal features that form the framework of the human body. Whether you’re learning basic human structure or building toward deeper medical knowledge, this quiz is your gateway to understanding how each part functions individually and as part of a coordinated whole. It’s more than a labeling exercise it’s about seeing the human form as an interconnected system of parts, regions, and functions.
The Body Parts Anatomy Quiz introduces learners to regions like the head, neck, torso, limbs, and their internal counterparts covering everything from muscles and bones to organs and joints. It highlights common terms like “abdomen” and “forearm,” while also reinforcing lesser-known anatomical references such as “antecubital” or “popliteal.” Each section uses visual logic and real-world associations to help students retain terminology, structure, and function. Whether you’re preparing for an exam, reviewing basic anatomy, or exploring your own physicality, this quiz provides a grounded and structured path forward.
This quiz format promotes not only recognition but understanding. You’ll see how the forearm connects to wrist motion, how the thorax protects vital organs, and how the pelvis anchors both the spine and legs. The result is a richer appreciation for how the human body is more than the sum of its parts it’s a masterwork of engineering, balance, and mobility.
Major Regions of the Human Body
The human body is often divided into axial and appendicular sections. The Body Parts Anatomy Quiz begins with these broad categories, asking learners to identify where the axial skeleton including the head, neck, and trunk — differs from the appendicular, which includes the upper and lower limbs. This foundational division helps organize all other anatomical structures and creates a roadmap for studying more detailed systems.
Each region serves a unique purpose. The trunk houses organs and serves as a platform for limb movement, while the limbs allow for interaction with the environment. The head contains sensory organs and the control center of the brain, while the neck connects it to the rest of the body, allowing for mobility and access for major blood vessels and nerves. This regional overview makes it easier to see how body parts function in concert rather than isolation.
Understanding body regions also helps in clinical settings. Terms like “thoracic,” “lumbar,” “brachial,” and “femoral” are not just academic they guide physical exams, surgery, and emergency care. The quiz reinforces these terms in a way that blends textbook knowledge with practical application, preparing learners for future study or real-life observation.
Upper Body: From Shoulder to Fingertips
The upper body consists of the shoulders, arms, forearms, wrists, and hands a sequence of highly mobile structures. In the Body Parts Anatomy Quiz, students learn how these regions transition from large, stabilizing joints to small, dexterous components. The shoulder (deltoid and acromial regions) connects the upper limb to the torso via the clavicle and scapula, providing a foundation for movement in every direction.
The arm and forearm are defined by two long bones the humerus and radius/ulna that support elbow flexion, rotation, and extension. Questions in this section help learners recognize how movement in one part affects others. The elbow’s hinge-like joint contrasts with the wrist’s range of motion, and these functional differences are highlighted throughout the quiz for better anatomical understanding.
The hand includes the carpal bones, metacarpals, and phalanges. These bones form the platform for grasp, fine motor skills, and tactile sensation. The quiz also introduces surface anatomy: identifying landmarks like the thenar eminence or anatomical snuffbox helps students relate textbook images to their own hands. This makes the anatomy not only easier to learn but also more tangible and relevant to everyday life.
Lower Body: Support, Movement, and Power
The lower body plays a critical role in support, locomotion, and posture. The Body Parts Anatomy Quiz explores this section in depth, starting with the pelvic region, where the sacrum and hip bones form a solid base for the spine and anchor the femurs. Understanding pelvic anatomy is crucial for biomechanics, childbirth, and core strength.
From the pelvis, the quiz moves down to the thigh (femoral region), knee (patellar and popliteal), leg (crural and sural), and ankle (tarsal), ending at the foot (plantar and dorsal). Each of these segments plays a role in mobility and stability. For example, the femur is the largest bone in the body and supports body weight during every step. The patella aids in knee extension by acting as a fulcrum for the quadriceps tendon.
The foot contains the tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges, all of which must absorb impact and adapt to various surfaces. The quiz helps students link this anatomy to real movement. You’ll better understand how flat feet, Achilles tendon injuries, or knee misalignment can affect balance, performance, and injury risk. This section integrates structural learning with biomechanical insight for long-term retention.
Internal Body Parts: Organs and Their Locations
No anatomy quiz would be complete without covering the major internal body parts. The Body Parts Anatomy Quiz identifies key organs lungs, heart, liver, kidneys, stomach, intestines and explains their position within the thoracic and abdominal cavities. Questions guide learners to associate organs with protective bones (like the rib cage) and landmarks (like the diaphragm) for better spatial memory.
The quiz reinforces basic organ function alongside anatomical location. For instance, it links the stomach to digestion, the lungs to gas exchange, and the kidneys to waste filtration. Students also learn to distinguish right vs. left anatomical references, a skill essential for interpreting images, conducting assessments, or studying pathology.
Knowing where organs reside also helps understand referred pain. For example, pain in the upper shoulder might signal gallbladder issues, while lower back pain may indicate kidney involvement. The quiz introduces this kind of thinking early, reinforcing how body parts do not operate in isolation they affect and reflect one another’s health and function.
Why the Body Parts Anatomy Quiz Matters
Understanding anatomy begins with knowing the names, positions, and relationships of body parts. The Body Parts Anatomy Quiz provides that foundation, building knowledge through visual logic and functional understanding. This is the type of learning that sticks because it links structure to everyday actions from breathing and sitting to typing or running.
This quiz is perfect for early learners, high school and college students, or even professionals needing a refresher. It covers not just labels, but regions, movements, and physiological relevance. Whether you’re preparing for nursing school, brushing up for a personal training certification, or simply curious about your body, this quiz supports growth through clarity and context.
Take the Body Parts Anatomy Quiz now and build a map of the human form. Every answer brings you closer to understanding what makes your body move, adapt, and thrive from head to toe.
Body Parts Anatomy – FAQ
The largest organ in the human body is the skin. It covers the entire body, protecting internal organs and regulating temperature. It also plays a vital role in sensation and immune defense. The skin consists of three layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue.
An adult human body typically contains 206 bones. These bones provide structure, protect organs, anchor muscles, and store calcium. Infants are born with approximately 270 bones, some of which fuse together as they grow.
The liver performs various essential functions, including detoxifying harmful substances, producing bile for digestion, and storing vitamins and minerals. It also plays a crucial role in metabolizing carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, making it vital for overall health.
The heart pumps blood through the body by contracting and relaxing in a rhythmic cycle. It has four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. Blood enters the atria, is pumped into the ventricles, and is then circulated to the lungs for oxygenation and through the body to deliver oxygen and nutrients.
The nervous system controls and coordinates body activities by transmitting signals between different body parts. It consists of the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system (nerves). The nervous system regulates voluntary actions, like movement, and involuntary actions, like heartbeat and digestion.
