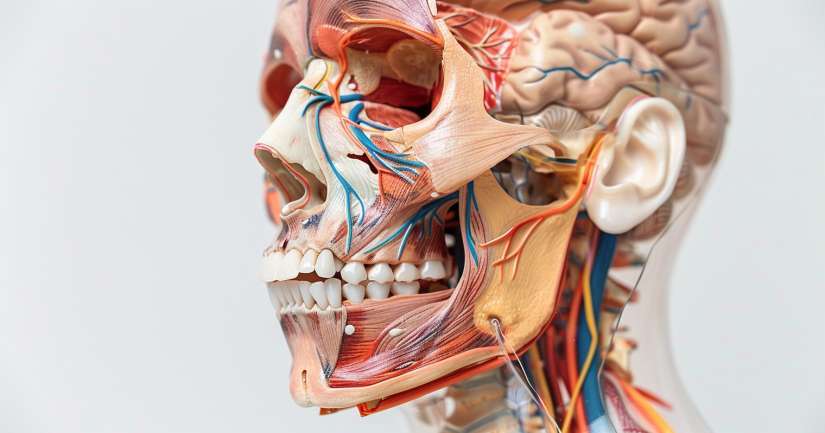
From the delicate web of cranial nerves to the layered muscles that control our every facial expression, the Head and Neck Anatomy Quiz shines a spotlight on the most intricate region of the human body. This area houses structures critical to breathing, speaking, chewing, hearing, and even balance all working in tight coordination within a space barely larger than a football. Mastering this quiz means gaining insight into a network of systems that influence everything from medical procedures to artistic portraiture.
The head and neck are anatomical crossroads, where major vessels, nerves, glands, and bones intersect with complex muscular and sensory systems. The Head and Neck Anatomy Quiz helps learners navigate this region with confidence, offering a guided tour through skeletal landmarks, muscle groups, major arteries, cranial nerves, and lymphatic drainage zones. This is more than a test of memory. It’s an exploration of how structure supports function in everything from swallowing and speech to eye movement and head posture. Whether you’re preparing for clinical practice or deepening your understanding of the human form, this quiz delivers a valuable, full-spectrum challenge.
This quiz is especially useful for students in medical school, dental training, physical therapy, speech-language pathology, or massage therapy. It also offers value for artists and animators working to capture human movement and realism. With layered diagrams, scenario-based questions, and system-level integration, it provides the ideal foundation for exploring one of the most clinically relevant areas in the entire body.
Cranial Bones and Facial Skeleton
The foundation of head anatomy begins with the skull, which consists of cranial bones that encase the brain and facial bones that support sensory organs and expression. The Head and Neck Anatomy Quiz highlights key bones like the frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, sphenoid, and ethmoid. Learners label the sutures that connect these bones coronal, sagittal, lambdoid, and squamous and examine how these landmarks are used in neurosurgery and radiology. Applied questions help students understand the implications of skull fractures and fontanelle closure in infants.
Moving forward, the facial skeleton includes the maxilla, mandible, zygomatic, nasal, lacrimal, palatine, inferior nasal conchae, and vomer bones. The quiz emphasizes how each contributes to the structure of the face and serves as anchor points for muscles, teeth, and sinuses. For example, questions explore how the maxillary sinuses relate to the orbit and how trauma to the zygomatic arch may affect chewing and ocular function. These structures are not just passive they provide shape, symmetry, and housing for vital organs.
Special attention is given to the mandible and its role in articulation and mastication. Students identify the condylar and coronoid processes, mandibular foramen, and mental foramen, tying each feature to functional and clinical relevance. By the end of this section, learners can visualize the bones of the head not as isolated pieces but as a coordinated architecture of protection, movement, and expression.
Muscles of the Head and Neck
Next, the quiz focuses on muscular anatomy from the broad platysma and sternocleidomastoid to the intricate muscles of mastication and facial expression. The Head and Neck Anatomy Quiz covers major muscle groups including the temporalis, masseter, buccinator, orbicularis oculi, orbicularis oris, and frontalis. Each muscle is paired with its origin, insertion, nerve supply, and action, building a full picture of how movement is created and controlled.
Questions in this section ask students to analyze expressions and match them to the correct muscle group. For example, what muscle elevates the corners of the mouth in a smile? Which one compresses the cheeks to help with chewing and speaking? These interactive elements strengthen the connection between anatomy and observable human behavior, while also aiding memory through functional context.
The neck is equally rich in muscular detail. Students identify the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius both important for head rotation and posture as well as deeper muscles like the scalene group and suprahyoid muscles. The quiz introduces clinical scenarios such as torticollis, muscle strain, and airway management during trauma. This section reinforces how understanding head and neck musculature is critical for both emergency care and daily human function.
Cranial Nerves and Sensory Function
No study of the head and neck would be complete without an in-depth look at the cranial nerves. The Head and Neck Anatomy Quiz includes all twelve cranial nerves, with emphasis on those that directly affect this region: the facial nerve (VII), trigeminal nerve (V), glossopharyngeal (IX), vagus (X), accessory (XI), and hypoglossal (XII). Each nerve is introduced with its path, branches, sensory or motor function, and clinical signs of damage.
Students label the three branches of the trigeminal nerve and explore how each innervates different parts of the face. Applied questions explore how Bell’s palsy affects facial symmetry or how trigeminal neuralgia causes shooting pain in response to simple stimuli. Visual diagrams help learners track nerve pathways through the foramen of the skull and into the tissues they serve.
This section also ties nerves to muscle control and reflexes. For example, which cranial nerves coordinate the gag reflex? What combination of motor and sensory nerves allows for speech, chewing, and swallowing? Through interactive reasoning, students deepen their understanding of how sensory and motor systems collaborate and what happens when they malfunction.
Vascular and Lymphatic Pathways
With so many vital structures in such a small space, vascular anatomy in the head and neck is both intricate and critically important. The Head and Neck Anatomy Quiz covers the carotid arteries, jugular veins, vertebral arteries, and their branches. Learners label the external and internal carotids, noting where they supply blood and how they relate to landmarks like the carotid sinus and bifurcation at the thyroid cartilage level.
Veins are equally important. Students trace the path of blood through the internal and external jugular veins, learning how drainage from the brain and superficial face returns to the heart. The quiz includes applied questions about blood pressure monitoring, carotid massage, and vascular access in emergency care. This makes the anatomy more than academic it becomes clinical, immediate, and practical.
In addition to blood vessels, lymph nodes and drainage pathways are introduced, especially in the context of infection, cancer metastasis, and routine physical examination. Questions ask students to identify deep cervical nodes, the submental triangle, and the significance of swelling near the parotid gland. This section encourages learners to visualize the flow of lymph and its importance in immune surveillance, diagnosis, and treatment planning.
Airway, Pharynx, and Swallowing
The head and neck are responsible for critical functions like breathing, speaking, and swallowing all of which involve overlapping structures and coordinated muscular action. The Head and Neck Anatomy Quiz includes labeling of the nasal cavity, oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, epiglottis, hyoid bone, and related cartilages. These features form a shared anatomical route for air and food, which must be precisely timed to avoid aspiration.
Students examine the three regions of the pharynx nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx and trace the pathway of air to the lungs versus food to the esophagus. The quiz reinforces how muscular and nervous systems coordinate actions like swallowing, coughing, and phonation. Applied questions focus on problems such as dysphagia, sleep apnea, or tracheostomy placement, showing how anatomical knowledge directly impacts patient care.
Special attention is given to the larynx, home to the vocal cords and key to voice production. Learners explore the roles of the thyroid, cricoid, and arytenoid cartilages, as well as the intrinsic muscles that adjust vocal fold tension. This section blends anatomy, physiology, and clinical application, making it ideal for learners in fields like speech-language pathology or anesthesiology.
Why the Head and Neck Anatomy Quiz Matters
The head and neck are regions where every millimeter matters. The Head and Neck Anatomy Quiz helps learners build a three-dimensional understanding of how all the systems in this area connect skeletal, muscular, vascular, nervous, and lymphatic. It’s more than just labeling bones and nerves. It’s about developing the ability to think spatially, reason clinically, and apply that knowledge in real-world settings, whether you’re drawing, diagnosing, or performing a procedure.
For healthcare students, this quiz reinforces material found in gross anatomy labs and clinical rotations. For artists and educators, it provides a concrete map of the structures that give the human form its most expres
Head And Neck Anatomy – FAQ
The primary structures of the head and neck include the skull, cervical spine, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, and glands. These components work together to support vital functions such as movement, sensation, and circulation. Key elements also include the brain, eyes, ears, nose, mouth, and throat.
The muscles of the neck, including the sternocleidomastoid, trapezius, and scalene muscles, facilitate a wide range of movements. These muscles allow for head rotation, flexion, extension, and lateral bending. They also play a crucial role in maintaining posture and supporting the head’s weight.
The cervical spine, consisting of seven vertebrae (C1-C7), is essential for supporting the head and protecting the spinal cord. It enables a wide range of head movements and provides structural stability. The cervical spine also contains intervertebral discs that act as shock absorbers, facilitating smooth and flexible motion.
The head and neck are primarily supplied by the carotid arteries and the jugular veins. The carotid arteries deliver oxygen-rich blood to the brain and facial structures, while the jugular veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart. These vessels are vital for maintaining proper circulation and oxygenation.
Nerves in the head and neck, including the cranial and spinal nerves, are responsible for transmitting sensory and motor signals. They facilitate functions such as vision, hearing, taste, and facial expressions. The vagus nerve, among others, plays a critical role in regulating autonomic functions like heart rate and digestion.
