Beneath every step, smile, heartbeat, and breath lies the silent force of contraction and the Muscle and Muscle Tissue Quiz is designed to uncover exactly how this biological machinery works. Muscle tissue isn’t just for bodybuilders or athletes. It plays a vital role in every movement, internal and external, voluntary and involuntary. From blinking and chewing to circulating blood and digesting food, the body’s muscular system operates 24/7, often without conscious thought.
The Muscle and Muscle Tissue Quiz explores more than surface-level anatomy. It dives into the molecular mechanisms of contraction, the cellular makeup of muscle tissue, and the physiological principles that power everything from marathon running to keeping your spine upright in a chair. It teaches the differences between skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle, and explains how muscle tissue grows, repairs, and adapts. For students aiming to enter medicine, physiotherapy, sports science, or personal training, mastering muscle tissue is essential because movement lies at the core of every human action.
Each question in this quiz asks students to think critically about structure and function. It’s not just about naming a muscle group, but understanding how it contracts, how it regenerates, and how different tissue types operate in sync. Whether you’re reviewing for an exam or just deepening your grasp of anatomy, this quiz will leave you with a much more complete view of the body in motion.
Types of Muscle Tissue
The human body contains three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Each one has distinct structures, locations, and functions. The Muscle and Muscle Tissue Quiz helps students learn to identify these types under a microscope, recognize where they occur, and understand how their roles differ. Skeletal muscle connects to bones and enables voluntary movement. It’s striated and multinucleated, designed for forceful, rapid contractions that can be consciously controlled.
Cardiac muscle, found only in the heart, is also striated but contains unique intercalated discs that allow synchronized contraction across the heart wall. This tissue is involuntary and resistant to fatigue, making it perfectly suited for nonstop function. Smooth muscle lacks striations and is found in the walls of hollow organs like blood vessels, intestines, and the bladder. It contracts slowly and rhythmically, controlled by the autonomic nervous system rather than conscious intent.
This quiz provides questions and visual references to help distinguish each type by both appearance and function. Students are asked to evaluate scenarios like a racing heart or a digestive spasm — and determine which muscle type is responsible. By the end of this section, learners will have a clear, practical grasp of how each tissue type contributes to homeostasis and body function.
Structure of Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle is perhaps the most familiar the biceps, quads, and calves we consciously flex but its internal structure is surprisingly intricate. The Muscle and Muscle Tissue Quiz dives deep into the hierarchy that makes this tissue so strong and adaptable. It begins with the entire muscle, then breaks down into fascicles (bundles), muscle fibers (cells), myofibrils, and finally sarcomeres the smallest contractile units.
Each sarcomere contains actin and myosin filaments, which slide past each other during contraction in a process known as the sliding filament theory. This process is triggered by calcium ions and powered by ATP. Students will learn how the neuromuscular junction plays a role in activating these contractions, and how acetylcholine is essential in passing the signal from nerve to muscle. The quiz reinforces this pathway by asking learners to trace an impulse from the brain to the actual contraction of a single muscle fiber.
The section also covers the supportive tissues that surround muscles: the epimysium (around the whole muscle), perimysium (around fascicles), and endomysium (around individual fibers). Understanding these layers is crucial in recognizing how force is distributed and how injuries like strains and tears can occur. This kind of detailed knowledge is especially useful for anyone studying sports medicine, rehabilitation, or physical therapy.
Physiology of Muscle Contraction
At the heart of muscle function is contraction a precise biochemical event involving electrical signals, ion gradients, and protein interaction. The Muscle and Muscle Tissue Quiz breaks this complex process into clear, manageable steps, beginning with the role of motor neurons. A single motor neuron and all the fibers it innervates form what’s called a motor unit, and these units vary in size depending on the muscle’s purpose. Large units are found in leg muscles; smaller, more precise ones control movements in the eyes and fingers.
The quiz leads learners through the sequence of events that causes a muscle to contract: the arrival of an action potential at the neuromuscular junction, the release of acetylcholine, the depolarization of the sarcolemma, calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and finally, the interaction of actin and myosin. This cascade requires energy, and students also explore how ATP is produced and used during sustained or high-intensity activity.
Muscle fatigue, oxygen debt, and recovery are also discussed. What happens when ATP runs low? How do anaerobic and aerobic pathways contribute? Why does lactic acid accumulate? The quiz presents real-life scenarios such as running a sprint or lifting weights to help students connect theory with practical muscle behavior, reinforcing both biochemical understanding and applied insight.
Muscle Growth, Repair, and Disorders
Muscle tissue has the remarkable ability to grow and adapt in response to stress, but it can also suffer from a wide range of disorders. The Muscle and Muscle Tissue Quiz covers how muscle fibers respond to training through hypertrophy, and how satellite cells aid in muscle repair after damage. It explains how muscle fibers differ in speed and endurance: slow-twitch (Type I) fibers for endurance, and fast-twitch (Type II) for power and speed.
Students also learn how resistance training, stretching, and nutrition affect muscle health. This section offers insight into how muscles adapt over time, making it useful for fields like kinesiology, physical education, or rehabilitation therapy. The quiz includes questions about anabolic processes, muscle protein synthesis, and the effects of overtraining or muscle wasting conditions such as cachexia or sarcopenia.
Disorders of the muscular system including muscular dystrophy, myasthenia gravis, and fibromyalgia — are introduced to show how and why muscle tissue may fail. These clinical examples emphasize the importance of muscle health in maintaining quality of life. Understanding the early signs of these disorders and their physiological basis helps students apply their knowledge to patient care or personal health management.
Why the Muscle and Muscle Tissue Quiz Matters
The Muscle and Muscle Tissue Quiz provides a well-rounded understanding of how muscles work, grow, and adapt. It offers students an essential foundation in anatomy and physiology by combining structural detail with real-world functionality. Whether you’re studying to become a nurse, therapist, coach, or personal trainer, this knowledge is a must-have for both theory and practice.
By completing this quiz, learners gain the ability to explain muscle contraction on a cellular level, distinguish between muscle tissue types, and assess how muscles respond to activity, stress, and disease. These insights don’t just improve academic performance they shape how we understand movement, performance, and health in everyday life.
Take the Muscle and Muscle Tissue Quiz today and discover how the body turns electrical signals into powerful movement, lasting strength, and precise control over everything you do.
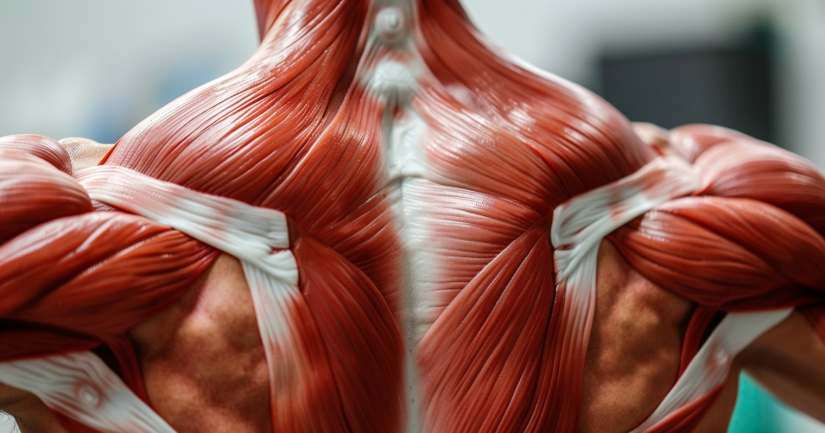
Muscle And Muscle Tissue – FAQ
Muscle tissue is a specialized tissue in the human body that has the ability to contract and generate movement. It is composed of muscle fibers, which are long, slender cells that can change length and produce force. There are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth.
Muscles grow and develop through a process called hypertrophy, which occurs when muscle fibers increase in size. This happens as a result of resistance training or other forms of exercise that place stress on the muscles. The body repairs and rebuilds the damaged fibers, making them thicker and stronger over time.
Each type of muscle tissue has a distinct role. Skeletal muscle, attached to bones by tendons, facilitates voluntary movement and posture. Cardiac muscle, found only in the heart, contracts to pump blood throughout the body. Smooth muscle, located in the walls of internal organs, regulates involuntary movements such as digestion and blood flow.
Maintaining healthy muscle tissue involves a balanced diet rich in protein, regular physical activity, and adequate rest. Protein provides the building blocks for muscle repair and growth, while exercise, especially strength training, stimulates muscle development. Sufficient rest allows for recovery and prevents overuse injuries.
Common issues include muscle strains, cramps, and chronic conditions such as muscular dystrophy. Muscle strains occur when fibers are overstretched or torn, often due to overexertion. Cramps are sudden, involuntary contractions that can cause severe pain. Muscular dystrophy is a group of genetic disorders characterized by progressive muscle weakness and degeneration.
