Are you ready to put your knowledge to the test? Our “Muscles Of Forearm Quiz” is here to challenge and educate you. This quiz offers a fantastic opportunity to deepen your understanding of forearm anatomy. You’ll discover the intricate details of each muscle, their functions, and how they work together seamlessly.
By participating, you’ll enhance your grasp of muscle locations and their roles in everyday movements. This can be incredibly beneficial for students, fitness enthusiasts, and anyone interested in human biology.
Expect questions that will make you think and recall information. Some might be easy, while others will test the limits of your knowledge.
Engaging in this quiz will not only test what you know but also highlight areas where you can improve. It’s a fun and interactive way to learn more about your body.
Ready to see how well you know the muscles of the forearm? Dive in and find out now!
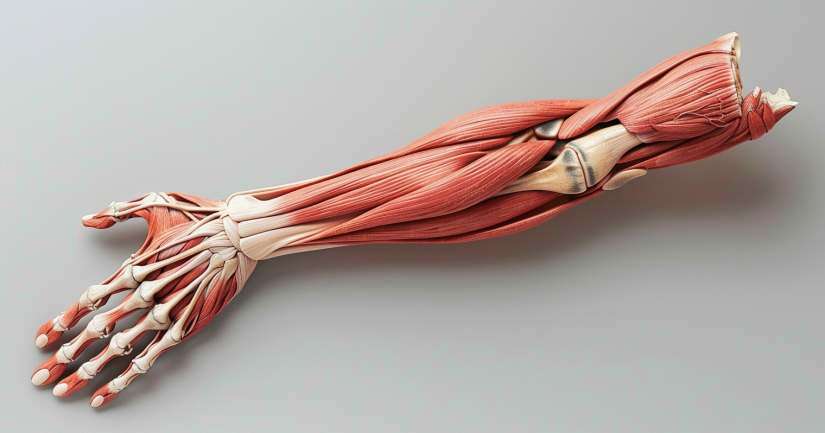
Muscles Of Forearm – FAQ
The forearm is composed of several muscles that can be broadly categorized into two groups: the flexors and the extensors. The flexor muscles are located on the anterior side of the forearm and are responsible for bending the wrist and fingers. The primary flexors include the flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, and flexor digitorum superficialis. On the posterior side, the extensor muscles, such as the extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi ulnaris, and extensor digitorum, extend the wrist and fingers.
The forearm muscles play a crucial role in a wide array of daily activities. They facilitate movements such as gripping, lifting, writing, and typing. Flexor muscles enable you to grasp objects firmly, while extensor muscles allow for the release and extension of the hand and fingers. Together, these muscles provide the dexterity and strength required for both fine motor skills and more strenuous tasks.
Common injuries affecting the forearm muscles include strains, tendinitis, and repetitive strain injuries (RSI). Strains occur when the muscles are overstretched or torn, often due to excessive lifting or abrupt movements. Tendinitis, the inflammation of tendons, can result from repetitive motions such as typing or playing sports. RSI is a broader category that encompasses various overuse injuries caused by repetitive tasks, leading to pain and discomfort in the forearm.
Strengthening the forearm muscles can be achieved through a variety of exercises. Wrist curls, both flexion and extension, are effective for targeting these muscles. Resistance bands and grip strengtheners can also be used to enhance muscle endurance and power. Consistency in performing these exercises, combined with proper form, will help in building stronger and more resilient forearm muscles.
When exercising the forearm muscles, it is important to start with lighter weights and gradually increase resistance to avoid strain. Proper warm-up and stretching routines can help prevent injuries. Additionally, maintaining good posture and ergonomics during daily activities can reduce the risk of overuse injuries. Listening to your body and not pushing through pain are crucial for long-term muscle health and overall well-being.
